| Cardiac Cath 4/6 |
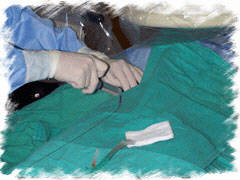 The
groin is infiltrated with a 1% to 2% lidocaine solution. Most patients
require conscious sedation and this varies with the preference of the
operator. The
groin is infiltrated with a 1% to 2% lidocaine solution. Most patients
require conscious sedation and this varies with the preference of the
operator. |
 The
artery is felt by the fingertips, and a needle is directed towards it
through a tiny hole, created with the tip of a scalpel. A thin-walled
needle is used for this purpose. The
artery is felt by the fingertips, and a needle is directed towards it
through a tiny hole, created with the tip of a scalpel. A thin-walled
needle is used for this purpose. When pulsatile blood flow is noted, a curved tip guide wire is then introduced into the needle and guided to the ascending aorta with intermittent use of fluoroscopy. |
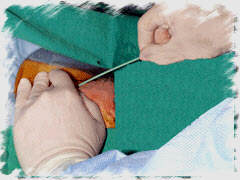 A
vascular access sheath is advanced over the guide-wire and placed in
the artery. The size of the sheath is dictated by the catheters that
will be employed in the case. Thus, a 6 French (F) sheath is used when
one anticipates the use of 6F catheters. Remember that 1 mm = 3F. Thus
a 6F system has an outer diameter of 6/3 = 2 mm. A
vascular access sheath is advanced over the guide-wire and placed in
the artery. The size of the sheath is dictated by the catheters that
will be employed in the case. Thus, a 6 French (F) sheath is used when
one anticipates the use of 6F catheters. Remember that 1 mm = 3F. Thus
a 6F system has an outer diameter of 6/3 = 2 mm. |
| |
|
The preformed left and right Judkin's catheters are most commonly employed to selectively engage the right and left coronary arteries. |
|
Under fluoroscopy, 1 - 2 ml of contrast is injected to confirm appropriate positioning of the catheter tip. Cineangiographic recordings are then made during the injection of approximately 5 to 9 ml of contrast. |
|
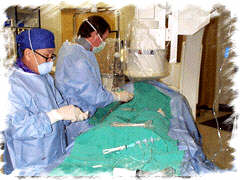
FOR AUDIO: Click the Speaker Icon to "unmute" Audio Throughout the procedure, the cardiologist constantly monitors the patient's pressure and EKG. Angios obtained during injection of the contrast is viewed on a second monitor (to the left of the cardiologist in the picture above).Pressures within the aorta and the left ventricle are also measured during the procedure. Blood samples may be drawn to assess their oxygen content, if needed in select cases. |
| |
|
|
| Cardiac Cath 4/6 |
 Through the sheath, and over a guide-wire, a pre formed (Judkin,
Amplatz or other) or multipurpose catheter is inserted and guided
towards the ostium of the coronary artery under fluoroscopic guidance.
The type of selected catheter is based upon operator preference and
may be modified on the basis of the patient's coronary artery anatomy.
Through the sheath, and over a guide-wire, a pre formed (Judkin,
Amplatz or other) or multipurpose catheter is inserted and guided
towards the ostium of the coronary artery under fluoroscopic guidance.
The type of selected catheter is based upon operator preference and
may be modified on the basis of the patient's coronary artery anatomy.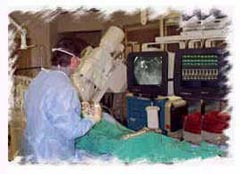 After
engaging the ostium of each coronary artery, the cardiologist confirms
that the pressure is not damped by a significant ostial narrowing
or because the catheter tip is against the wall of the artery. Forceful
injection in the latter situation can create a coronary artery dissection
when contrast is pushed into the subintimal portion of the artery.
After
engaging the ostium of each coronary artery, the cardiologist confirms
that the pressure is not damped by a significant ostial narrowing
or because the catheter tip is against the wall of the artery. Forceful
injection in the latter situation can create a coronary artery dissection
when contrast is pushed into the subintimal portion of the artery.